Products
CRP Rapid Quantitative Test Kit
|
CRP Rapid Quantitative Test Kit |
|
|
Canine C-reactive Protein Rapid Quantitative Test Kit |
|
| Catalog number | RC-CF33 |
| Summary | The canine C-reactive protein rapid quantitative test kit is a pet in vitro diagnostic kit that can quantitatively detect the concentration of C-reactive protein (CRP) in dogs. |
| Principle | fluorescence immunochromatographic |
| Species | Canine |
| Sample | Serum |
| Measurement | Quantitative |
| Range | 10 - 200 mg/L |
| Testing Time | 5-10 minutes |
| Storage Condition | 1 - 30º C |
| Quantity | 1 box (kit) = 10 devices (Individual packing) |
| Expiration | 24 months after manufacturing |
| Specific Clinical Application | The cCRP analyzer provides in-clinic results for canine C-Reactive Protein, useful at various stages in canine care. The cCRP can confirm the presence of underlying inflammation during a regular check-up. If therapy is needed, it can continuously monitor the efficacy of treatment to determine disease severity and response. After surgery, it is a useful marker of surgery-related systemic inflammation and can help with clinical decision-making during recovery. |
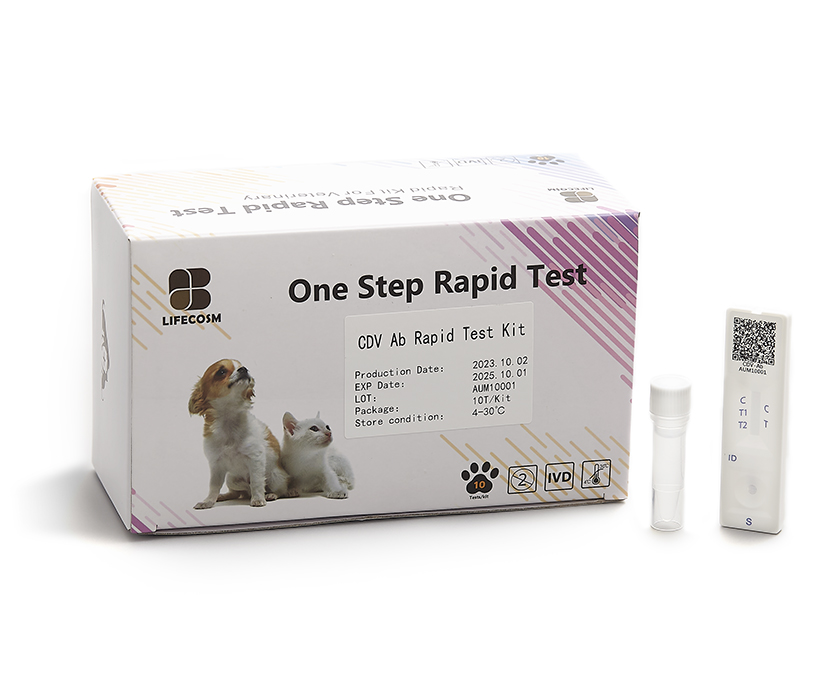
Canine Distemper Virus
A Simple Test to Check for C-Reactive Protein in Dogs
C-Reactive Protein (CRP) normally exists at a very low concentration in healthy dogs. After an inflammatory stimulation such as infection, trauma or illness, the CRP can increase in just 4 hours. Testing at the onset of an inflammatory stimulation can guide critical, proper treatment in canine care. The CRP is a valuable test that provides a real-time inflammatory marker. The ability to have follow-up results can indicate the canine’s condition, helping determine recovery or if further treatments are necessary.
What is C-reactive protein (CRP)1?
• Major acute-phase proteins (APPs) produced in the liver
• Exists at very low concentrations in healthy dogs
• Increase within 4~6 hours after inflammatory stimulus
• Rising 10 to 100 times and peaking within 24–48 hours
• Decreases within 24 hours after resolution
When does CRP concentration increase1,6?
Surgery
Preoperative Assessment, Monitoring Response to Treatment, and Early Detection of Complications
Infection (bacteria, virus, parasite)
Sepsis, Bacterial enteritis, Parvoviral infection, Babesiosis, Heartworm infection, Ehrlichia canis infection, Leishmaniosis, Leptospirosis, etc.
Autoimmune Diseases
Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia (IMHA), Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (IMT), Immune-mediated polyarthritis (IMPA)
Neoplasia
Lymphoma, Hemangiosarcoma, Intestinal adenocarcinoma, Nasal adenocarcinoma, Leukemia, Malignant histiocytosis, etc.
Other Diseases
Acute pancreatitis, Pyometra, Polyarthritis, Pneumonia, Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), etc.