Products
High definition Giardia Antigen Test Kit - Lifecosm Canine Parvo Virus Ag/Canine Distemper Virus Ag Test Kit Veterinary medicine – Lifecosm
High definition Giardia Antigen Test Kit - Lifecosm Canine Parvo Virus Ag/Canine Distemper Virus Ag Test Kit Veterinary medicine – Lifecosm Detail:
LSH Ab Test Kit
|
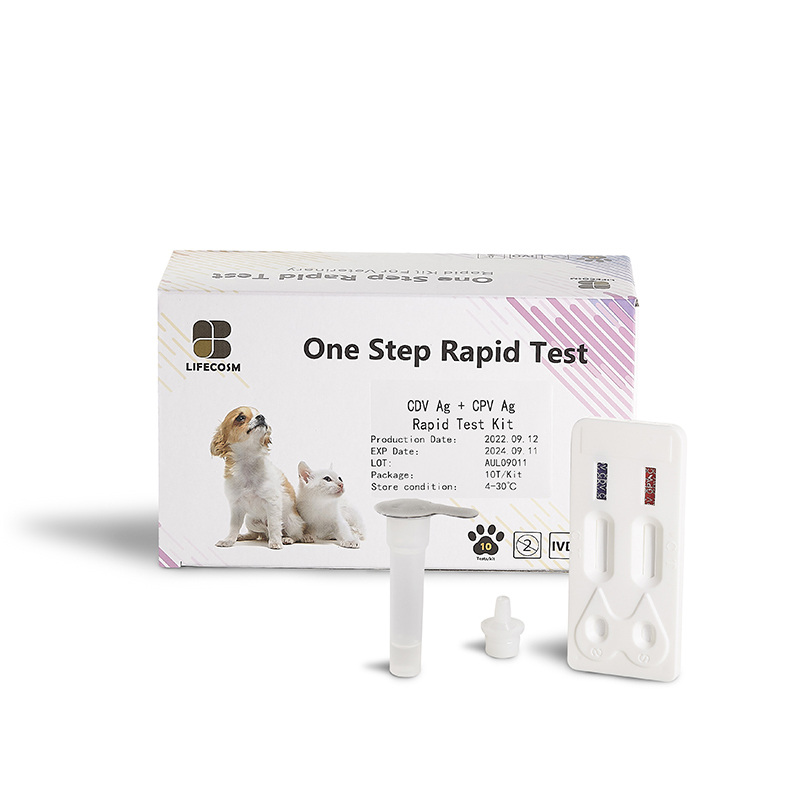
Canine Distemper Virus+ Parvo Virus Ag Test Kit |
|
| Catalog number | RC-CF06 |
| Summary | Detection of specific antigens of canine distempervirus and parvo virus within 10 minutes |
| Principle | One-step immunochromatographic assay |
| Detection Targets | Canine Distemper Virus (CDV+ CPV) antigens |
| Sample | Canine ocular discharge and nasal discharge |
| Reading time | 10~ 15 minutes |
| Sensitivity | 98.6 % vs. RT-PCR |
| Specificity | 100.0 %. RT-PCR |
| Quantity | 1 box (kit) = 10 devices (Individual packing) |
| Contents | Test kit, Buffer bottles, Disposable droppers, and Cotton swabs |
| Storage | Room Temperature (at 2 ~ 30℃) |
| Expiration | 24 months after manufacturing |
|
Caution |
Use within 10 minutes after openingUse appropriate amount of sample (0.1 ml of a dropper)
Use after 15~30 minutes at RT if they are stored under cold circumstances Consider the test results as invalid after 10 minutes |
Information
Canine distemper poses a severe threat to dogs, in particular puppies, which are severely exposed to the disease. When infected, their fatality rate reaches 80%. Adult dogs, though rarely, can be infected with the disease. Even cured dogs suffer from long-lasting harmful effects. The breakdown of the nervous system can aggravate the senses of smell, hearing, and sight. Partial or general paralysis can be easily triggered, and complications such as pneumonia can occur. However, canine distemper is not transmitted to human beings.

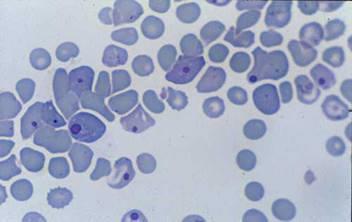

>> Inclusion bodies composed of virus nucleocapsids are dyed in blue with red and white cells.
>> Excessive formation of keratin and para- keratin on the sole of a foot devoid of hairs is shown.
Symptoms
Canine distemper is easily transmitted to other animals through viruses. The disease can occur through contact with the discharges of respiratory organs or urine and feces of infected puppies.
There are no specific symptoms of the disease, a main reason for the ignorance or delay of treatment. Common symptoms include a cold with high fever that could develop into bronchitis, pneumonia, gastritis, and enteritis. In early stage, squint, bloodshot eyes, and eye mucus are an indicator of the disease. Weight loss, sneeze, vomiting, and diarrhea are also easily examined. In late stage, viruses infiltrating the nervous system trigger partial or general paralysis and convulsion. Vitality and appetite can be lost. If the symptoms are not severe, the disease can deteriorate with no treatments. Low fever only can occur for two weeks. Treatment is hard after several symptoms including pneumonia and gastritis are shown. Even if the infection symptoms disappear, the nervous system may malfunction several weeks later. The rapid proliferation of viruses causes the formation of keratins on the sole of a foot. The fast examination of puppies suspected of suffering from the disease is recommended according to the various symptoms.
Prevention and treatment
Puppies which recover from a virus infection are immune from it. However, it is very rare for the puppies to survive after being infected with the virus. Therefore, vaccination is the safest way.
Puppies born of dogs immune against canine distemper have immunity from it, too. The immunity can be obtained from milks of mother dogs during several days after birth, but it is different depending on the amount of antibodies that the mother dogs have. After that, the immunity of puppies decreases rapidly. For the appropriate time for vaccination, you should seek consultation with veterinarians.
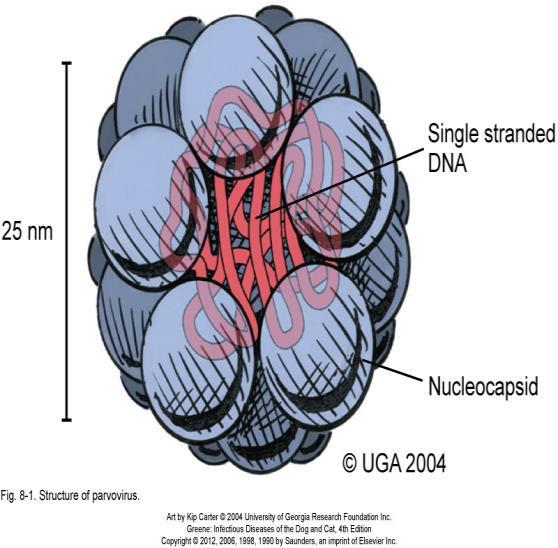
Canine Parvovirus
Information
In 1978 was known a virus which infected dogs regardless of
age to damage enteric system, white cells, and cardiac muscles. Later, the virus was defined as canine parvovirus. Since then,
the outbreak of the disease has been on the rise worldwide.
The disease is transmitted through direct contacts among dogs, in particular in places like dog training school, animal shelters, playground and park etc. Even though canine parvovirus does not infect other animals and human beings, dogs can be infected by them. Infection medium is usually the feces and urine of infected dogs.
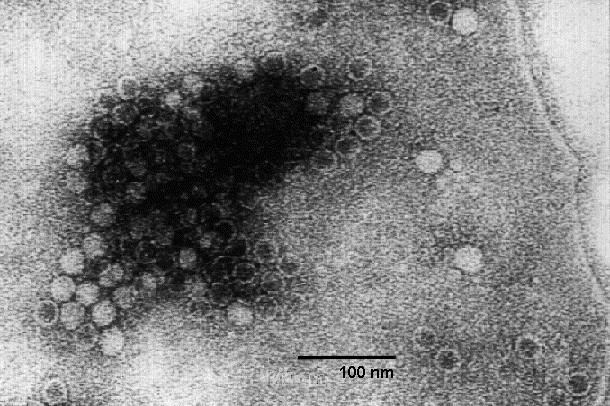
Canine parvovirus. Electron Micrograph by C Büchen-Osmond. Http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ ICTVdb/ICTVdB/50110000.htm
C
How can I know my dogs are infected with canine parvovirus?
The first symptoms of the infection include depression, appetite loss, vomiting, severe diarrhea, and the increase in temperature of the rectum. The symptoms occur 5~7 days after infection.
The feces of the infected dogs become light or yellowish gray.
In some cases, fluid-like feces with blood can be shown. Vomiting and diarrhea causes dehydration. Without treatment, dogs suffering from them can die of fit. Infected dogs usually die 48~72 hours after showing the symptoms. Or, they could recover from the disease without complications.
In the past, most of the puppies below the age of 5 months and 2~3 % of adult dogs died of the disease. However, the fatality rate has sharply decreased due to vaccination. Nevertheless, puppies younger than 6 month- old dogs are at high risk of being infected with the virus.
Diagnosis and treatment
Various symptoms including vomiting and diarrhea are the symptoms used in diagnosing sick dogs. Fast transmission in a short period of time raises the possibility that canine parvovirus is the cause for the infection. In this case, the examination of feces of the sick dogs can bring to the light the cause. This diagnosis is carried out in animal hospitals or clinical centers.
Until now, there are no specific medicines to eliminate all viruses in the infected dogs. Therefore, early treatment is critical in curing infected dogs. The minimization of electrolyte and water loss is helpful for preventing dehydration. Vomiting and diarrhea should be controlled and antibiotics should be injected into the sick dogs to avoid second infection. More importantly, a close attention should be paid to the sick dogs.
Prevention
Regardless of age, all dogs must be vaccinated against canine parvovirus. Continuous vaccination is necessary when the immunity of dogs is not known.
Cleaning and sterilization of kennel and its surroundings are very important
in preventing the spread of viruses.
Be careful that your dogs do not contact the feces of other dogs.
In order to avoid the contamination, all feces must be managed properly. This effort should be done with all people participating to maintain the neighborhood clean.
In addition, consultation by experts like veterinarians is essential in the prevention of the disease.
Product detail pictures:


Related Product Guide:
It adheres to the tenet Honest, industrious, enterprising, innovative to develop new products constantly. It regards customers, success as its own success. Let us develop prosperous future hand in hand for High definition Giardia Antigen Test Kit - Lifecosm Canine Parvo Virus Ag/Canine Distemper Virus Ag Test Kit Veterinary medicine – Lifecosm , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Morocco, Doha, Mali, With the aim of compete with good quality and develop with creativity and the service principle of take customers' demand as orientation, we will earnestly provide qualified products and good service for domestic and international customers.
Hope that the company could stick to the enterprise spirit of Quality, Efficiency, Innovation and Integrity, it will be better and better in the future.