Products
Lifecosm Avian lnfectious Bursal Disease Ag Rapid Test Kit for veterinary diagnostic test
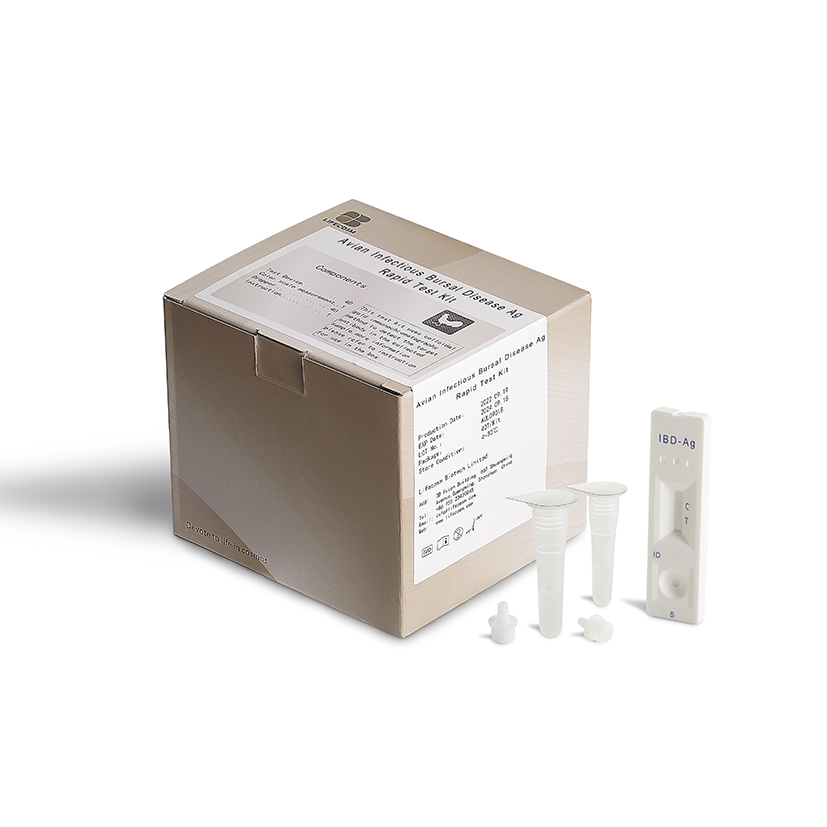
Avian lnfectious Bursal Disease Ag Rapid Test Kit
| Avian lnfectious Bursal Disease Ag Rapid Test Kit | |
| Summary | Detection of specific Antigen of Avian lnfectious Bursal Disease within 15 minutes |
| Principle | One-step immunochromatographic assay |
| Detection Targets | Avian lnfectious Bursal Disease Antigen |
| Sample | Chicken Bursa |
| Reading time | 10~ 15 minutes |
| Quantity | 1 box (kit) = 10 devices (Individual packing) |
| Contents | Test kit, Buffer bottles, Disposable droppers, and Cotton swabs |
|
Caution |
Use within 10 minutes after opening
Use appropriate amount of sample (0.1 ml of a dropper) Use after 15~30 minutes at RT if they are stored under cold circumstances Consider the test results as invalid after 10 minutes |
Information
Infectious bursal disease (IBD), also known as Gumboro disease, infectious bursitis and infectious avian nephrosis, is a highly contagious disease of young chickens and turkeys caused by infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV),[1] characterized by immunosuppression and mortality generally at 3 to 6 weeks of age. The disease was first discovered in Gumboro, Delaware in 1962. It is economically important to the poultry industry worldwide due to increased susceptibility to other diseases and negative interference with effective vaccination. In recent years, very virulent strains of IBDV (vvIBDV), causing severe mortality in chicken, have emerged in Europe, Latin America, South-East Asia, Africa and the Middle East. Infection is via the oro-fecal route, with affected bird excreting high levels of the virus for approximately 2 weeks after infection. The disease is easily spread from infected chickens to healthy chickens through food, water, and physical contact.
Clinical signs
Disease may appear suddenly and morbidity typically reaches 100%. In the acute form birds are prostrated, debilitated and dehydrated. They produce a watery diarrhea and may have swollen feces-stained vent. Most of the flock is recumbent and have ruffled feathers. Mortality rates vary with virulence of the strain involved, the challenge dose, previous immunity, presence of concurrent disease, as well as the flock's ability to mount an effective immune response. Immunosuppression of very young chickens, less than three weeks of age, is possibly the most important outcome and may not be clinically detectable (subclinical). In addition, infection with less virulent strains may not show overt clinical signs, but birds that have bursal atrophy with fibrotic or cystic follicles and lymphocytopenia before six weeks of age, may be susceptible to opportunistic infection and may die of infection by agents that would not usually cause disease in immunocompetent birds.
Chickens infected with the disease generally have the following symptoms: pecking at other chickens, high fever, ruffled feathers, trembling and slow walking, found lying together in clumps with their heads sunken towards the ground, diarrhea, yellow and foamy stool, difficulty in excretion, reduced eating or anorexia.
The mortality rate is around 20% with death within 3–4 days. Recovery for survivors takes about 7–8 days.
The presence of maternal antibody (antibody passed to the chick from the mother) changes the disease's progression. Especially dangerous strains of the virus with high mortality rates were first detected in Europe; these strains have not been detected in Australia.[5]
ORDER INFORMATION