Products
Lifecosm Newcastle disease Virus Ag Rapid Test kit for veterinary diagnostic test
Newcastle disease Virus Ag Rapid Test kit
| Summary | Detection of specific Antigen of Newcastle disease
within 15 minutes |
| Principle | One-step immunochromatographic assay |
| Detection Targets | Newcastle disease Antigen |
| Sample | cloaca |
| Reading time | 10~ 15 minutes |
| Quantity | 1 box (kit) = 10 devices (Individual packing) |
| Contents | Test kit, Buffer bottles, Disposable droppers, and Cotton swabs |
|
Caution |
Use within 10 minutes after opening
Use appropriate amount of sample (0.1 ml of a dropper) Use after 15~30 minutes at RT if they are stored under cold circumstances Consider the test results as invalid after 10 minutes |
Information
Newcastle disease, also known as the Asian fowl plague, is caused by a virus of chicken and a variety ofbirds acute highly contagious disease, mainly characterized by difficulty in breathing, diarrhea, nervous disorders, mucosal and serosal bleeding. Because of different pathogenic strains, can be expressed as the severity of the disease vary widely.
Clinical signs
Egg drop after a (otherwise asymptomatic) Newcastle disease infection in a duly vaccinated broiler parent flock
Signs of infection with NDV vary greatly depending on factors such as the strain of virus and the health, age and species of the host.
The incubation period for the disease ranges from 4 to 6 days. An infected bird may exhibit several signs, including respiratory signs (gasping, coughing), nervous signs (depression, inappetence, muscular tremors, drooping wings, twisting of head and neck, circling, complete paralysis), swelling of the tissues around the eyes and neck, greenish, watery diarrhoea, misshapen, rough- or thin-shelled eggs and reduced egg production.
In acute cases, the death is very sudden, and, in the beginning of the outbreak, the remaining birds do not seem to be sick. In flocks with good immunity, however, the signs (respiratory and digestive) are mild and progressive, and are followed after 7 days by nervous symptoms, especially twisted heads.
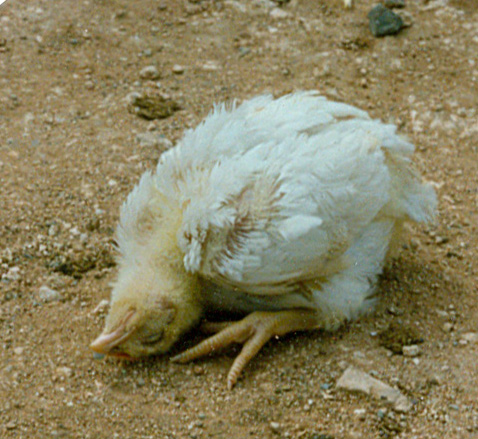

Same symptom in a broiler
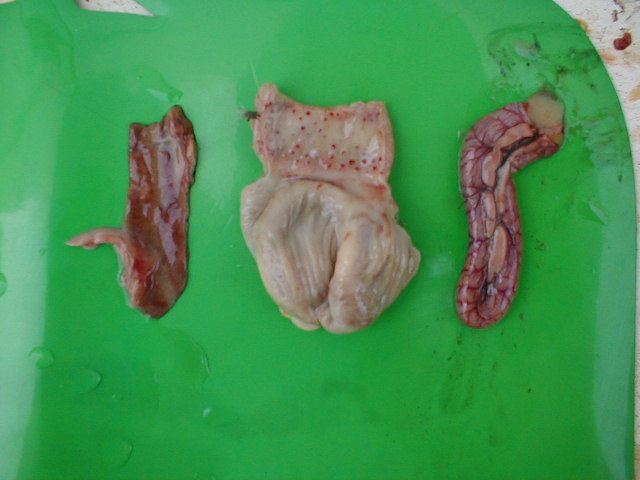
PM lesions on proventriculus, gizzard, and duodenum
Order Information